Our thyroid gland is a small butterfly shaped organ located at the base of our neck, just below the larynx box or Adam’s apple. This little organ goes a long way in regulating the functions and processes of various systems in our body like digestive system, nervous system, genitourinary system, musculoskeletal system and cardiovascular system.
WORDS ABRAHAM MATHEW SAJI
Think of your body as a car and the thyroid gland as the engine. Just as the engine powers speed, the thyroid produces hormones that regulate how fast your body runs.
A CLOSER LOOK AT THE THYROID GLAND
Iodine and Thyroid Hormones
The thyroid uses iodine (from food like iodized salt, milk, seafood) to make two hormones:
- T4 (thyroxine) – storage form
- T3 (triiodothyronine) – active form that drives metabolism
T4 is mostly converted into T3 in organs like the brain, liver, and kidneys.
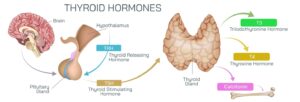
The Thyroid Gland’s Connection with the Pituitary Gland
The thyroid itself gets instructions from the pituitary gland, which releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) — basically, the body’s accelerator pedal.
When the thyroid works well, so does the rest of you. But when it’s overactive or underactive, things quickly go off balance.
More Quick Facts
- Thyroid dysfunction rises with age.
- 200+ million people worldwide have thyroid disorders — half of them do not know it.
- Women are up to 10 times more likely than men to be affected.
- In Malaysia, about 10% have hypothyroidism, while 2% hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid issues can complicate pregnancy and sometimes be life-threatening.
WARNING SIGNS OF THYROID TROUBLE
- Sleep changes, anxiety, fatigue
- Sensitivity to cold or excessive sweating
- Hair thinning, brittle nails, dry skin
- Unexplained weight gain or loss
- Memory problems, poor concentration
- Irregular periods, infertility, miscarriage
If you notice several of these, check in with your doctor.
COMMON THYROID DISORDERS
- Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid → rapid heartbeat, sweating, weight loss
- Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid → fatigue, dry skin, feeling cold
- Goiter: Enlarged thyroid causing swelling, trouble breathing or swallowing
- Thyroid nodules: Usually harmless lumps, rarely cancerous
- Thyroid cancer: Lump, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s): Autoimmune damage leading to hypothyroidism
- Graves’ disease: Autoimmune hyperthyroidism, often with eye problems
- Postpartum thyroiditis: Thyroid changes after pregnancy
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Doctors may check your family history, medications, and run tests like blood work, ultrasound, or fine-needle biopsy.
Treatment depends on the condition, and can include:
- Medications
- Hormone replacement
- Lifestyle changes
- Radioactive iodine
- Surgery
| This article is part of our series on health issues that can affect the thyroid gland. |