Beware the Blood Suckers!
April 28, 2022 Return
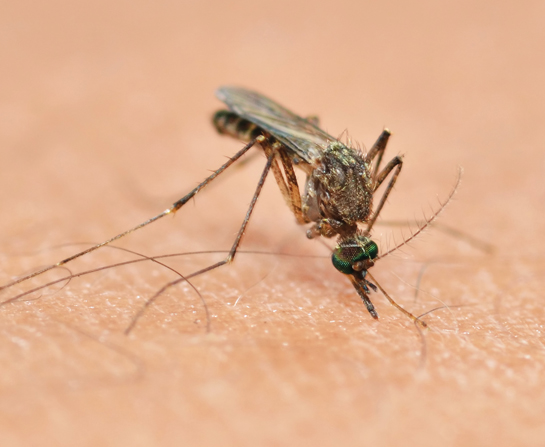

What is Japanese Encephalitis?
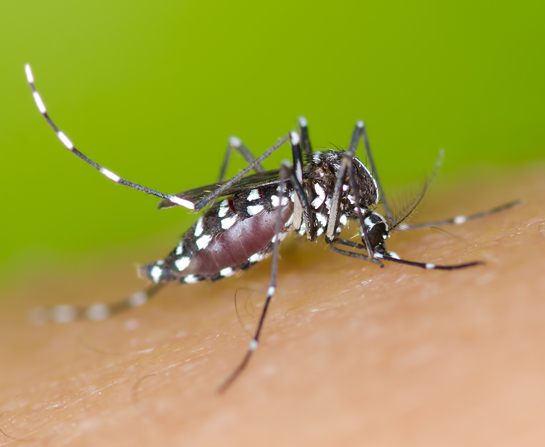
Japanese Encephalitis (JE) is an infectious disease, which is caused by a type of virus called flavivirus. Flavivirus belongs to the same virus sub-family or genus as the dengue virus. Mosquitoes can spread JE virus to people and are called vectors.
When people are infected with JE virus, they usually have mild symptoms including fever and headache. But some, approximately one in 250, may develop severe symptoms as the infection spreads to the brain, with rapid onset of high fever, headache, neck stiffness and disorientation. They will most likely to end up in a coma and might even die. If they recover from these severe symptoms, 20%-30% are likely to suffer permanent nerve-related problems like paralysis, fits and the inability to speak.
The scary part of JE is that although doctors can detect JE viablood tests, there is no antiviral treatment for now. So, prevention is the best option when it comes to JE.
How does JE spread?
Pigs and water birds such as herons are the main hosts for the JE virus. Infected animals serve as reservoirs for the JE virus; the virus multiplies in huge numbers in these animals, which have been important sources of outbreaks in Malaysia.
Your household mosquito, including three Culex species, is the main vector that transports the JE virus from these animals to humans. When a Culex mosquito bites an animal infected with JE virus, the virus is transferred to the mosquito through the blood. When the infected mosquito bites a person, the person is then infected with the JE virus. The virus subsequently multiplies in the infected person and causes illness.
Prevention tips
- Do ensure you keep your house and its surroundings clean and clear of mosquito-breeding places. Clear, stagnant water – even as little as one teaspoon – can breed hundreds of those bloodsuckers.
- Vaccinate yourself against JE. This is especially if you are living near construction sites, swamps, farms or other places that are conducive for mosquito breeding or are sources of JE virus. You may even plan to travel to countries where JE is common. In those cases, it’s best for you to consult your doctor for the vaccination.
References:
1. Centre for Health Protection. Available at www.chp.gov.hk
2. Go YY, et al. (2014). Zoonotic encephalitides caused by arboviruses: transmission and epidemiology of alphaviruses and flaviviruses. Clin Exp Vaccine Res.; 3(1):58-77.
3. WHO. Available at www.who.int
If you like this article, do subscribe here.