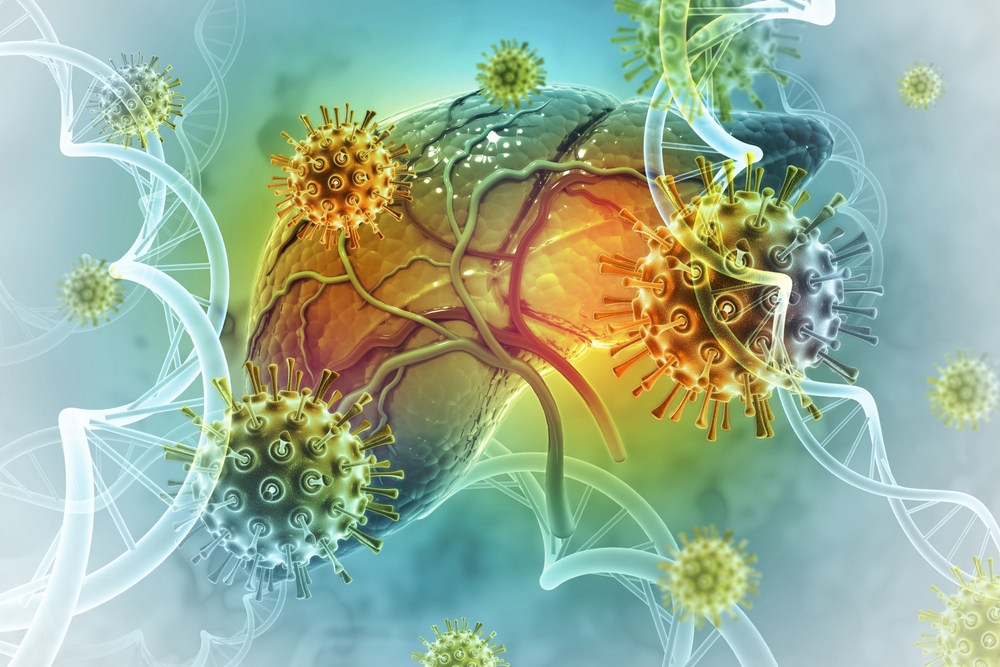
Our liver is one of the major internal organs of our body that works nonstop to purify our blood as well as to produce and store essential micronutrients that are required by our body. When the liver is infected or sore, it fails to perform its functions, and this results in the signs and symptoms manifested by hepatitis.
WORDS ABRAHAM MATHEW SAJI
The word hepatitis is a combination of hēpar or hēpat, which means “liver” in ancient Greek, and itis, the Greek word for inflammation.
Thus, hepatitis means inflammation of the liver.
CAUSES OF HEPATITIS
- Inflammation of the liver can be caused by various conditions, illnesses, some foods and drinks, certain medications, and also viruses.
- Speaking about viruses, virus types A, B, C, D, E, F and G have been reported to cause infectious hepatitis.
- The most common are hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- Of these, HBV and HCV can cause chronic hepatitis that can lead to conditions of liver cirrhosis and also liver cancer if left untreated.
HEPATITIS A
- More common in places with poor hygiene and sanitation conditions.
- Hepatitis A infections are often mild and can be treated easily compared to the others.
- After treatment and recovery, one can become immune to the virus.
- There is also a safe and effective vaccine available.
HEPATITIS B AND C
Can be caused by one or more of the following:
- Sharing needle with infected person
- Having unprotected sex with infected person
- Sharing personal items like toothbrush and razor blade with infected person
- Receiving a blood transfusion from an infected person
- Having a tattoo created using an unsterile or infected needle
- Bitten by an infected person
- Through lactation from an infected mother
- When the virus enters through a break in the skin.
Both HBV and HCV infections are treatable, depending on the severity of the infection.
There is a vaccine available to protect us from HBV. However, there is no vaccine yet against HCV.
INCUBATION PERIOD
From the time when a person is infected with the virus to the development of symptoms is known as the incubation period.
Each type of virus has varying incubation periods:
- 15 to 45 days for HAV
- 45 to 160 days for HBV
- 14 to 180 days for HCV
SYMPTOMS OF ACUTE HEPATITIS
At the initial stages — also referred to as acute phase — some of the common symptoms are:
- Mild to moderate fever
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue muscle and joint aches
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
SYMPTOMS OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS
When the acute phase is left untreated, the disease progresses to the long-term or chronic phase with the following symptoms:
- Moderate to high fever
- Abdominal swelling
- Swelling of lower extremities of the body
- Yellowness of skin, eyes and tongue (jaundice)
- Blood in vomit or faeces
- Itchy skin
- Dark urine
- Hives
HOW HEPATITIS IS DIAGNOSED
The diagnosis of the type and degree of infection can be done by thorough laboratory investigations like:
- Pathological blood tests that can detect the levels of enzymes, proteins and antibodies.
- Pathological nucleic acid tests that can confirm the type of virus and its numbers.
- Scans that can detect inflammation and any damage to surface of the liver.
- Paracentesis, where a sample of the abdominal fluid is extracted and tested.
- Liver biopsy that can detect cancer and extent of liver damage.
- Elastography that measures stiffness of the liver.
- Liver function tests that can help to identify liver disease.
TREATMENT OPTIONS
There is a wide array of treatment options available today and will depend on factors like:
- Type of infection
- Degree of infection
- Age and other underlying conditions of the person
The treatment dose and duration may also be prolonged based on any or more of the above factors.
Advances in research have seen treatment options moving from chemical-based medications to biotechnological interventions like monoclonal antibodies.
PREVENTION
As the old adage goes: “An ounce of prevention is better than a pound of cure.”
Some of the steps we can take to prevent being infected by hepatitis viruses are:
- Avoid injecting illegal substances into our body.
- Avoid sharing of needles, toothbrushes, razors and other personal care items.
- Practice safe sex.
- Wash hands properly with soap and water after using the toilet.
- Consume safe drinking water.
- Eat clean and fresh foods.
- Ensure needles used in body piercing or tattoo have been sterilized.
- Avoid or drink moderate amounts of alcohol.
- If you have not been vaccinated, talk to the doctor about whether you should get your shots.
| This article is part of our series on health issues that can affect the liver. |