WORDS DR JAMIE JOSEPH
 FEATURED EXPERT FEATURED EXPERTDR JAMIE JOSEPH Consultant Rehabilitation Medicine Specialist Sunway Medical Centre Velocity |
Cerebral palsy can develop as a result of damage or abnormalities in developing brain that could occur before, during, or after birth.
While specific symptoms can vary widely from person to person, such damage to the brain can lead to physical limitations that will affect the person’s ability to move and perform everyday tasks, such as:
- Weakness
- Spasticity
- Loss of motor control
- Limited coordination
MOST PEOPLE LIVING WITH CEREBRAL PALSY WILL NORMALLY EXHIBIT ISSUES SURROUNDING WALKING AND COORDINATION
Typically, most children with cerebral palsy will have delayed gross and fine motor skills.
This means that the child with mild motor deficits tend to master how to sit, stand, and/or walk at a later age as compared to their normal peers.
Some children with cerebral palsy may not even achieve these milestones.
CHALLENGES WITH MOVEMENT FOR INDIVIDUALS LIVING WITH CEREBRAL PALSY
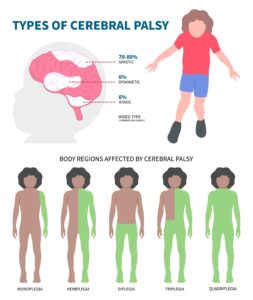
Cerebral palsy can involve:
- All 4 limbs (quadriplegic cerebral palsy),
- Both lower limbs (diplegic cerebral palsy),
- Half of the body (Hemiplegic cerebral palsy), or
- Abnormal movement (Dyskinetic cerebral palsy)
Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy
- Those with quadriplegic cerebral palsy most of the time also develop cognitive function issues.
- These individuals face the most challenge when it comes to trying to walk or move around (ambulation).
- Though some in this group may be able to walk when they are younger, many may lose their mobility in the older teens or young adults due to poorly controlled spasticity with or without bony deformities.
Diplegic and Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy
- Affected individuals have fewer impairments compared to those living with quadriplegic cerebral palsy. Hence, they have a much better chance of ambulation.
- Most people with diplegic cerebral palsy may require walking aids and orthosis to ambulate.
- People with hemiplegic cerebral palsy usually has more favourable recovery or improvement in ambulation, as only one of their lower limbs is affected.
ROBOTIC TRAINING AS AN EFFECTIVE MEANS TO IMPROVE THE MOBILITY OF PEOPLE WITH CEREBRAL PALSY
Robotic training can provide the following benefits:
- Improve their affected individual’s coordination
- Improve their balance
- Increase their muscle strength
- Improve their endurance
These improvements can be achieved through a constant pattern of repetitive, high-intensity, and goal-oriented training—which is key in improving their mobility.
WHAT ARE THE ROBOTIC TECHNOLOGIES AVAILABLE IN MALAYSIA?
Gait rehabilitation robots fall into 2 categories:
- End effectors: stationary devices that use foot plates to guide feet and reproduce the specific way in which a person walks (gait pattern).
- Exoskeletons: ‘wearable’ robots that provide an over-ground walking experience for patients. Truncal training and balance robotics are available in the market to focus on improving sitting balance and posture.
Key Benefits of Robotics
- High intensity repetitive movement and a constant gait pattern that can only be administered via this technology.
- This repetition has the potential to induce effective brain organization also known as neuroplasticity.
- The use of robotics lessens the work force and decreases the labour-intensive approach when compared to manually performed gait retraining.
For best outcomes, robotics-assisted therapy is carried out alongside conventional physical therapy.
Potential Side Effects and Complications of Robotics-Assisted Therapy
- Pressure ulcer formation, bruising or injury at the location(s) that the skin comes in contact with the machine.
- Injuries to the joint, muscles, or tendons due to misalignment between human joint and exoskeletal joint.
- People with cerebral palsy and limited mobility may have osteoporosis even at a young age, so they face a risk of bone fracture.
These Related Risks Can Be Managed With a Multidisciplinary Approach
- A rehabilitation physician will evaluate the individual to ensure suitability of robotic therapy.
- The medical team will assess and carry out appropriate management measures to account for the individual’s spasticity and contracture before letting the individual start their robotics-assisted rehabilitation.
- A trained and skilled operator will be present during each session to minimize unwarranted injury on the individual’s skin or joint.
| This article is part of our series on rehabilitation and medical innovations. |