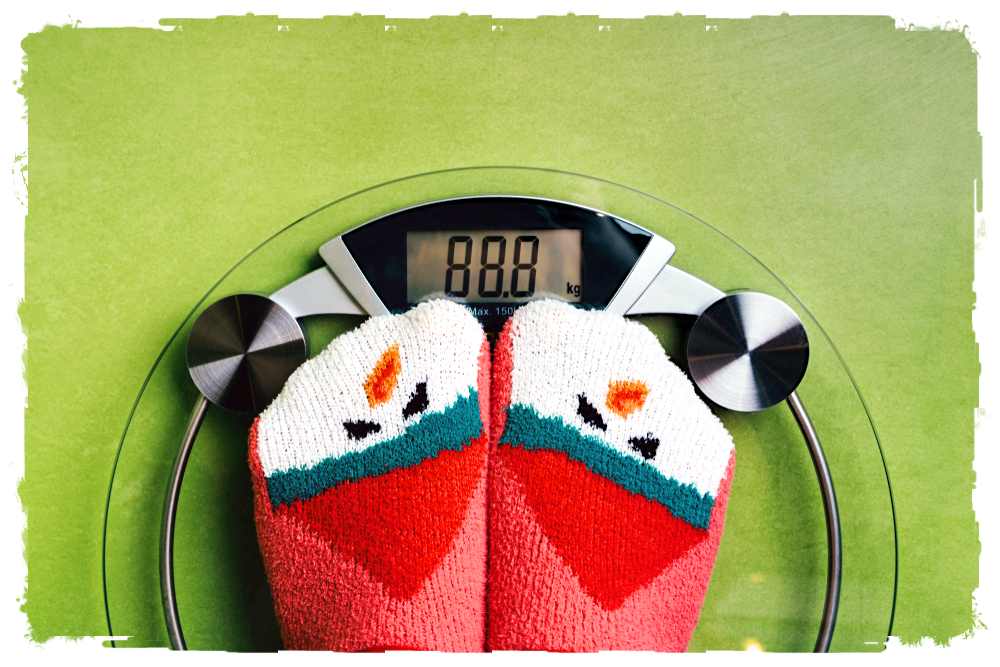
Obesity is considered a disease, and that’s a good thing—it means doctors can treat it with science-backed methods. From lifestyle changes to medical options, people get real help, not just blame or quick fixes.
WORDS PROFESSOR DR NORLAILA MUSTAFA
 FEATURED EXPERT FEATURED EXPERTPROFESSOR DR NORLAILA MUSTAFA Consultant Endocrinologist Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz UKM |
OBESITY AS A CHRONIC DISEASE
‘Disease’ is defined as any harmful deviation from the normal structure or functional state of an individual or organism, which is usually associated with certain signs and symptoms.
‘Chronic disease’ is described as a long-lasting condition with persistent effects that affect one’s social and economic consequences and eventually their quality of life.
Given these two definitions, it is right to acknowledge obesity as a chronic disease.
People with obesity often suffer from other medical conditions, the more common ones listed in the table on this page.
Obesity is also associated with an increase in death from any disease, complication, accident, or exposure (all-cause mortality).
COMMON MEDICAL CONDITIONS PRESENT IN PEOPLE WITH OBESITY
- Hypertension or high blood pressure
- Dyslipidaemia or high levels of fats in the blood
- Type 2 diabetes
- Coronary heart disease
- Gallbladder disease
- Mechanical problems such as back pain and knee pain
CLASSIFYING OBESITY AS A CHRONIC DISEASE CAN IMPROVE ITS PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT
Most chronic diseases, also called non-communicable diseases or NCDs for short, occur due to a combination of genetic, psychological, environmental, and behavioural factors.
Obesity is a chronic disease that affects people of all age groups. Therefore, identifying individuals that are at risk because of the aforementioned factors will help in reducing the prevalence of obesity in Malaysia.
Prevention
Those at risk to become obese are men and women that are already overweight.
Early behavioral changes through the adoption of a healthy lifestyle would prevent them from becoming obese individuals.
Similarly, overweight individuals should also be screened for the presence of co-morbidities like hypertension, dyslipidaemia, diabetes, and coronary heart disease.
Treatment
People with obesity can be treated immediately once they are recognized and diagnosed early. This will prevent further health complications that are associated with obesity.
Management of obesity in the early stage can easily be done on an outpatient basis in any health clinic without the need to see a specialist.
At the clinic, one will be screened for the probable cause of their obesity, as well as receive advice on adopting an appropriate diet and taking up suitable physical activities.
A STANDARDIZED APPROACH FOR RESEARCH, CLINICAL PRACTICE & MORE
Classifying obesity as a chronic disease allows for more focused research into causes and treatment of obesity, systematic implementation of clinical practice guidelines for standardized medical approaches based on approved best practices, and formation of a scientific blueprint for national anti-obesity campaigns.
| The 2nd edition of Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Obesity was published in 2023. It is developed to guide healthcare professionals on how best to approach and manage patients with overweight and obesity, based on latest medical evidence. Interested parties can get a digital copy at the Academy of Medicine of Malaysia website by clicking on this link (link opens in a new tab). |
| This article is part of our series on effective and research-based weight loss strategies. |