Vaping remains one of today’s most debated health topics, clouded by mixed messages, myths, and controversy. To help clear the air, a pharmacist offers an unbiased look at the science and facts behind e-cigarettes, so you can make informed choices about this habit.
WORDS LIM TECK CHOON
 FEATURED EXPERT FEATURED EXPERTLIM KELVIN Masters in Diabetes Care Pharmacist & Principal Trainer CARiNG Pharmacy |
Vaping isn’t new, as this habit dates all the way back to the 1930s. However, its rising popularity, along with claims by some quarters that it is the healthier alternative to smoking, causes vaping to remain a subject of controversy.
In 2024, pharmacist Lim Kelvin took an unbiased, in-depth look at the practice of vaping based on available evidence at the ‘Breathful Beginnings: Rise Above Smoke’ webinar organized by the Monash University Pharmacy Society. We’re pleased to share with you the details of his talk.
UNDERSTANDING VAPING
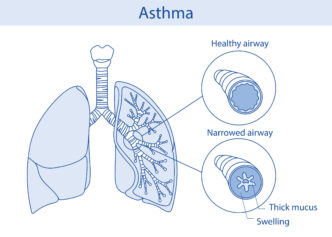
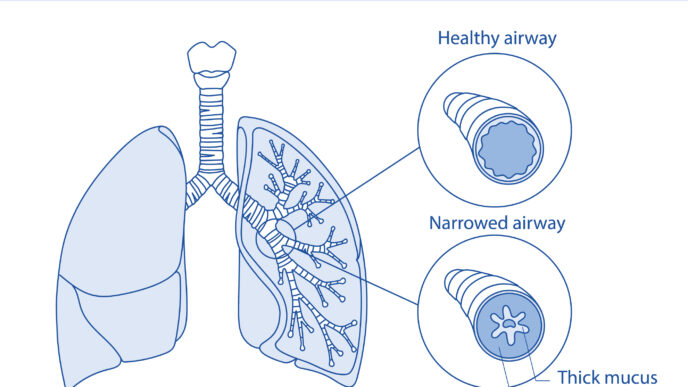
Pharmacist Lim Kelvin explains that vaping refers to the act of inhaling vapours produced by an electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) or similar device.
E-cigarettes are one type of electronic nicotine delivery system (ENDS). Other types of ENDS include:
- Vape pens
- Pod systems
- Tanks
- Mods
These devices are often collectively referred to as vapes, though they differ in design, nicotine content, and functionality.
When We Think of Vapes, We’re Usually Thinking of E-Cigarettes
“E-cigarettes are battery-powered devices designed to simulate the experience of smoking without burning tobacco,” Lim Kelvin elaborates.
What the e-cigarette does is heat a liquid solution, commonly referred to as e-liquid or vape juice, to create an aerosol that users inhale. This process gives rise to the term ‘vaping’.
WHY IS VAPING SO POPULAR?
Easily Customizable
Many vaping devices allow users to adjust variables such as temperature, power output, and airflow, giving them control over their vaping experience.
A Variety of Flavours
Younger users, especially, find this appealing.
Flavours range from traditional tobacco and menthol to fruits, desserts, and even novelty flavors.
Perception of Reduced Harm
Many people perceive vaping as a less harmful alternative to traditional smoking.
However, as we will explore later, this perception is not entirely accurate.
Vaping comes with its own set of risks and concerns!
Smoking Cessation Aid
Some smokers turn to vaping as a method to quit or reduce their consumption of traditional cigarettes.
While there is some evidence supporting this use, it remains a topic of debate in the medical and public health communities.
WHY IS IT CONTROVERSIAL?
Vaping Can Be Used to Deliver Illegal and Hazardous Substances
These substances include:
- Nicotine
- Cannabis or weed
| Recreational use of cannabis is illegal in Malaysia. |
Potential Safety Uses with the E-Cigarette

- Battery safety. Poor quality or damaged batteries can pose fire and explosion risks.
- Coil head material. The coil vapourises the vape juice. The choice of metals used in the coil can affect the release of potentially harmful substances when heated.
- E-liquid ingredients. The safety profile of various flavourings and additives when inhaled is not fully understood and remains a subject of ongoing research.
- Device regulation. The lack of standardized regulations in many regions means that the quality and safety of e-cigarette components can be inconsistent.
Potential Safety Issues with the Vape Juice or E-Liquid
- Vape juice or e-liquid is the liquid that is converted into aerosol by an e-cigarette or other vaping devices.
- It’s typically a mixture of water and food-grade flavouring along with either nicotine, cannabis, propylene glycol (PG, a food additive), or vegetable glycerin (VG, a sugar alcohol).
- PG and VG are used to produce smoke that simulate the tobacco cigarette smoke.
- If flavour is prioritised, higher levels of PG are added into the e-liquid. If plume, or the shape and amount of smoke, is prioritized, then the levels of VG will be higher.
“Simply put, every Tom, Dick, and Harry can sell and make their own e-liquid,” Lim Kelvin says, “and this lack of regulation is a safety issue.”
- The infamous vitamin E acetate is a prime example. This substance is implicated as a possible cause of e-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury (EVALI, see below).
- Improper mixing of ingredients can produce harmful compounds in the e-liquid. For example, heating certain flavours or additives can generate toxic substances such as formaldehyde or acetaldehyde, which are known to cause cancer.
- Unqualified mixers could improperly handle or inaccurately measure nicotine, leading to dangerously high levels of nicotine in the e-liquid. This can cause nicotine poisoning, especially in new or non-smokers, and increase the addiction potential of the e-liquid.
ARE E-CIGARETTES REALLY BETTER THAN CIGARETTES?
Both have their share of health risks. Let’s compare.
| CIGARETTES | E-CIGARETTES |
| Contains 69 known cancer-causing substances. | No tar or carbon monoxide present but may contain some cancer-causing substances. |
| Nicotine is always present. | Nicotine may be present in varying concentrations. |
| Tobacco-specific nitrosamines (TSNAs) are potent chemicals that can cause cancer. | TSNAs either absent or present in trace amounts. |
| Produces volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can increase the risk of lung airway products. | VOCs present in lower levels than cigarettes, but some (like formaldehyde) may be produced when e-liquid is overheated. |
| Poisonous heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, and arsenic are present. | Metal particles may be present due to heating coils, wicks, and other components. |
| Unstable free radicals and other products that can damage cells and may cause cancer are produced. | These are likely present in lower amounts. |
| No flavouring. | Flavouring present. Some are linked to health issues, such as diacetyl being linked to popcorn lung disease. |
| No propylene glycol or vegetable glycerin. | Propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin included to produce vape fumes; can be toxic at high levels. |
IS E-CIGARETTE AN EFFECTIVE MEANS TO QUIT SMOKING?
Lim Kelvin points to a ‘living review’—a systematic review which is continually updated to incorporate relevant new evidence as it becomes available—conducted by the Cochrane group.
Vaping May Help Smokers Quit the Habit, but It Is Not Effective in Keeping Them Nicotine-free
The latest data, published in 2024, found the following:
- There is high-certainty evidence that e-cigarettes with nicotine increase quit rates compared to nicotine replacement therapy NRT.
- While this sounds good at first, most studies found that only 10% to 20% of people that vaped as a smoking cessation method remained nicotine-free after 3 to 6 months.
“This review suggests that while vaping may be more effective than NRT in helping people quit smoking,” Lim Kelvin tells us. “However, it also can result in continued nicotine use rather than complete cessation.”
E-CIGARETTE OR VAPING PRODUCT USE-ASSOCIATED LUNG INJURY (EVALI)
- EVALI is short for ‘E-cigarette or Vaping product use-Associated Lung Injury’.
- It is a serious respiratory illness that has been linked to vitamin E acetate from vaping or using e-cigarette products.
- Vitamin E acetate can interfere with normal lung functioning when inhaled.
- In 2020, the average EVALI prevalence in the US was 1.4 cases per 100,000 people between 12 and 64 years old.
- After the recommendation to stay away from vitamin E acetate was instituted, EVALI cases dropped sharply.
SO… TO VAPE OR NOT TO VAPE?
Lim Kelvin points out that there are 4 valid reasons to say no to vaping.
- Vaping can lower the threshold to become addicted to nicotine.
- People that assume vaping is not harmful or less harmful to smoking can be lulled into becoming addicted to the substances present in e-juices.
- People that vape can be more susceptible to using harsher substances such as marijuana.
- Lack of proper and correct regulation of vape products means the pitfalls of vaping outweigh any perceived benefits.
HOW TO QUIT SMOKING WITHOUT RESORTING TO VAPING
Lim Kelvin reveals that nicotine replacement therapy or NRT has a 55% quit rate.
- NRT is available at most pharmacies and clinics.
- NRT can be very effective, but it’s most successful when combined with other support like counseling or behavioral therapy.
- All these can be achieved by working closely with a doctor or a pharmacist, as well as joining a support group or seeing a counsellor.
So, if you wish to quit smoking:
- Choose a quit date.
- Inform your friends and family of your intention to quit.
- Remove all reminders of smoking such as ashtrays and lighters.
- Work with your pharmacist or doctor on a plan to identify and avoid triggers for craving as well as what to do when craving hits you.
- Stock up on NRT supplies.
- Establish support networks (supportive friends and family members, support group).
- Develop new healthy habits to replace smoking.
- Set up a reward system for milestones reached (1-week smoke-free, 1 month smoke-free, etc).
| This article is part of our series on smoking, vaping, the effects of these activities on our health, and how to quit the habit. |
References:
- Hartmann-Boyce, J., Lindson, N., Butler, A. R., McRobbie, H., Bullen, C., Begh, R., Theodoulou, A., Notley, C., Rigotti, N. A., Turner, T., Fanshawe, T. R., & Hajek, P. (2022). Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation. Cochrane library, 2023(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd010216.pub7
- Friedman A. S. (2021). Association of vaping-related lung injuries with rates of e-cigarette and cannabis use across US states. Addiction (Abingdon, England), 116(3), 651–657. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.15235