WORDS ANAS ALMASWARY & PROFESSOR DR SUZANA SHAHAR
FEATURED EXPERTS
 ANAS ALMASWARY ANAS ALMASWARYMaster’s Student in Clinical Nutrition Faculty of Health Sciences Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM) |
 PROFESSOR DR SUZANA SHAHAR PROFESSOR DR SUZANA SHAHARDietetic Program Centre for Healthy Aging and Wellness Faculty of Health Sciences Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM) |
When we feel a scratchy throat or struggle to breathe, our first thought is usually hospitals. But what if I told
you there’s a simple remedy in your kitchen?
Let’s explore how the anti-inflammatory diet can actually boost our immune system, especially when it comes to respiratory health.
THE TROUBLE WITH PRO-INFLAMMATORY DIETS
Our body’s immune system is like a superhero that fights off infections and heals injuries, and inflammation is its natural power.
But here’s the twist: if not kept in check, inflammation can turn into a villain that causes chronic diseases. Hence, the foods we consume can either be a superhero sidekick or a troublemaker!
A pro-inflammatory diet influences our immune system’s balance in bad way, increasing the inflammation in our body.
Such a diet, measured by the Adapted Dietary Inflammatory Index (ADII), is associated with systemic inflammation and reduced kidney function in older adults. Chronic low-grade inflammation is believed to be one possible pathway linking this dietary pattern to kidney dysfunction.
EXAMPLES TO PRO-INFLAMMATORY FOODS
|
Researchers found that a higher ADII is related to higher levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a marker of inflammation, and lower estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR), an indicator of kidney function.
Hence, a proinflammatory diet can lead to both systemic inflammation and reduced kidney function.
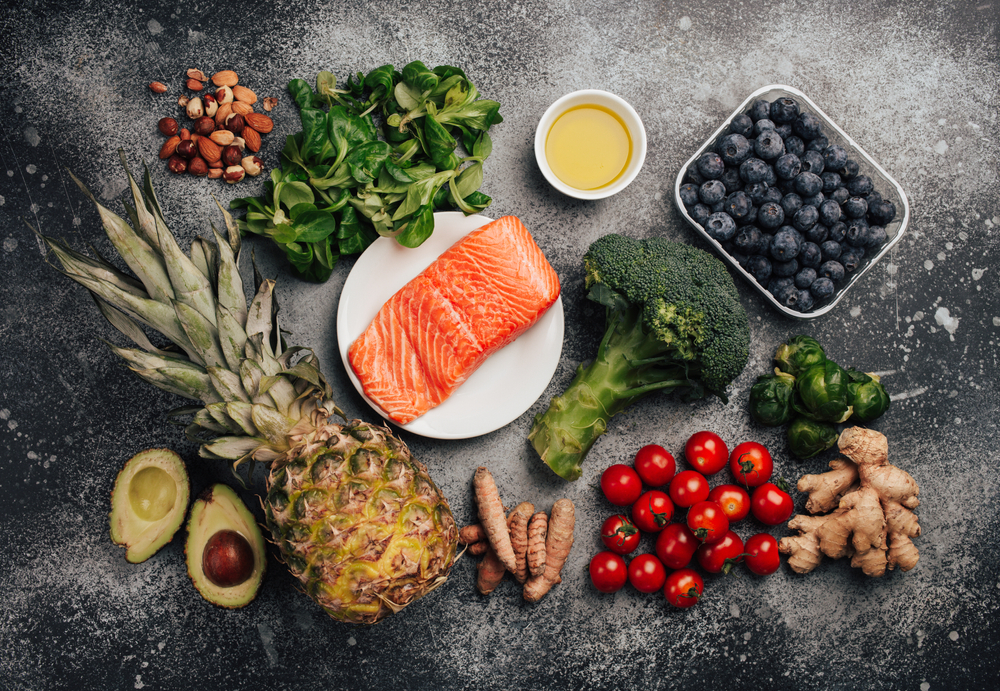
THE BENEFITS OF AN ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DIET
Generally, an anti-inflammatory diet should include sources of low-fat protein, colourful no- starchy carbohydrates, healthy fats like extra virgin olive oil, supplementation of omega 3 fatty acids, and foods rich in polyphenols.
An anti-inflammatory diet keeps insulin levels stable and cuts down on omega 6-fatty acids, which is crucial for beating silent inflammation.
Found in vibrant non-starchy veggies and fruits, polyphenols included in this diet put the brakes on inflammation by targeting a key player called nuclear factor (NF-κB). These polyphenols activate AMP kinase, a central switch controlling metabolism, including blood sugar levels.
The anti-inflammatory diet goes the extra mile by reducing chronic inflammation at the cellular level and tweaking gene expression. The result is lower risk of chronic diseases like obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes.
| NUTRIENTS | EXAMPLES OF FOODS | TIPS |
| Lean sources of proteins | Chicken, fish, or protein-rich vegetarian sources like tofu or legumes. |
Consume approximately the size and thickness of the palm of your hand. |
| Colourful carbohydrates | Vegetables like broccoli, spinach, carrots, bell peppers; fruits like guava and dragon fruits. | Fill two-thirds of your plate with non-starchy vegetables and substantial amounts of fruits These foods will help maintain a low glycemic load and provide adequate levels of polyphenols. |
| Healthy fats | Vegetable oils. | Use in cooking or drizzle over salads and vegetables. |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines. | Avoid deep frying; omega-3 fatty acids will be lost if you do this. |
References:
- Bikman, B. (2020). Why we get sick: The hidden epidemic at the root of most chronic disease–and how to fight it. BenBella Books.
- Eleazu C. O. (2016). The concept of low glycemic index and glycemic load foods as panacea for type 2 diabetes mellitus; prospects, challenges and solutions. African health sciences, 16(2), 468–479. https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v16i2.15
- Estruch R. (2010). Anti-inflammatory effects of the Mediterranean diet: The experience of the PREDIMED study. The proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 69(3), 333–340. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665110001539
- Galland L. (2010). Diet and inflammation. Nutrition in clinical practice : official publication of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 25(6), 634–640. https://doi.org/10.1177/0884533610385703
- Grimes, K. (2011). The everything anti-inflammation diet book: The easy-to-follow, scientifically-proven plan to reverse and prevent disease lose weight and increase energy slow signs of aging live pain-free. Simon and Schuster.
- Lyons, C. L., & Roche, H. M. (2018). Nutritional Modulation of AMPK-Impact upon Metabolic-Inflammation. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(10), 3092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103092
- O’Neil, A., Shivappa, N., Jacka, F. N., Kotowicz, M. A., Kibbey, K., Hebert, J. R., & Pasco, J. A. (2015). Pro-inflammatory dietary intake as a risk factor for CVD in men: A 5-year longitudinal study. The British journal of nutrition, 114(12), 2074–2082. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515003815
- Oprea, E. (2021). The power plate diet: Discover the ultimate anti-inflammatory meals to fat-proof your body and restore your health. Rodale Books.
- Rudnicka, E., Suchta, K., Grymowicz, M., Calik-Ksepka, A., Smolarczyk, K., Duszewska, A. M., Smolarczyk, R., & Meczekalski, B. (2021). Chronic low grade inflammation in pathogenesis of PCOS. International journal of molecular sciences, 22(7), 3789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073789
- Sears B. (2015). Anti-inflammatory diets. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 34 Suppl 1, 14–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2015.1080105
- Shivappa, N., Bonaccio, M., Hebert, J. R., Di Castelnuovo, A., Costanzo, S., Ruggiero, E., Pounis, G., Donati, M. B., de Gaetano, G., Iacoviello, L., & Moli-sani study Investigators (2018). Association of proinflammatory diet with low-grade inflammation: results from the Moli-sani study. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.), 54, 182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.04.004
- Xu, H., Sjögren, P., Ärnlöv, J., Banerjee, T., Cederholm, T., Risérus, U., Lindholm, B., Lind, L., & Carrero, J. J. (2015). A proinflammatory diet is associated with systemic inflammation and reduced kidney function in elderly adults. The journal of nutrition, 145(4), 729–735. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.114.205187