In Malaysia, flu can occur year-round. Older persons, especially those with chronic diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure, are advised to make flu vaccination an annual priority, especially during the holiday seasons when mingling and traveling are often inevitable. It’s important to strike a balance between staying safe and creating beautiful memories!
DO YOU KNOW THAT YOU COULD END UP WITH A HEART ATTACK OR STROKE WHEN YOU GET THE FLU?
Recent studies have cautioned that influenza increases the risk of heart attack by more than 10 times in the first 7 days after contracting the flu.
This is especially so if you are 65 and over, regardless of whether you have a history of heart disease or are living with chronic illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, lung disease and kidney disease. In industrialized countries, most deaths associated with flu occur among older persons aged 65 years and above!
Among older persons, influenza can present as a relatively mild respiratory illness; it may also present without any symptoms (no fever and/or no cough). It can also lead to fatigue and confusion, potentially setting off a sequence of catastrophic events.
Professor Datuk Dr Zulkifli Ismail, Technical Committee Chairman of the Immunise4Life Programme, explains: “It is not just a fever, runny nose, cough and body aches, it could seriously harm your heart.”
HOW THE FLU AFFECTS YOUR HEART
When the flu virus enters your system, your immune system strings into action.
Just like fights in real life, collateral damage may result; when an infection triggers a strong response from your immune system, the immune cells can also damage your own healthy tissues and organs.
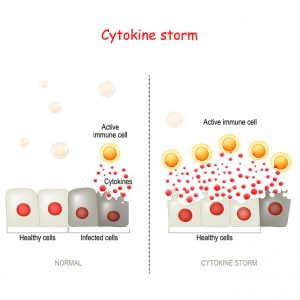
One example is COVID-19, which can trigger very high activation of the immune system, resulting in the uncontrolled release of cytokines, small molecules that aid cell-to-cell communication in immune responses and stimulate the movement of cells towards sites of infection.
This uncontrolled release (“cytokine storm”) may lead in failure and death of many organs in the body.
Studies suggest that the same inflammatory response described above can trigger effects that can damage the heart (cardiovascular events) when you have an influenza infection.
Dr Alan Fong, the President of the National Heart Association Malaysia (NHAM) and a consultant cardiologist, shares that your body’s immune response, when present along the direct effects of flu on the inner lining of your blood vessels or atherosclerotic plaques, may cause rupture of such plaques or blockage in the arteries–effects that can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
OLDER PERSONS ARE ESPECIALLY AT RISK WHEN THEY CATCH THE FLU
In older persons, there are changes that occur in the immune system that leads to a decline in the ability of the body to fight off infections such as the flu; this is known as immunosenescence.
Professor Dr Tan Maw Pin, a consultant geriatrician that chairs the Flu & Older Persons Sub-Committee of the Malaysian Influenza Working Group (MIWG), tells us: “In addition to this, ageing contributes to chronic, non-infectious, low-grade inflammation—known as inflammaging—which plays a key role in the cause and progression of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases.”
She further adds that ageing also promotes the development and progression of atherosclerosis, the most common cause of acute coronary syndrome. This syndrome gives rise to situations in which the blood supplied to the heart is suddenly blocked.”
“Hence, when an older person gets the flu, all these factors put them at higher risk of developing a heart attack and stroke,” Prof Tan reiterates.
FLU VACCINATION CAN PROTECT YOUR HEART

Studies have found that the flu vaccination was associated with a 34% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, and those that have recent acute coronary syndrome had a 45% lower risk.
There is also an 18% reduced risk of death reported in patients with heart failure.
For people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, studies have shown that the flu vaccination reduces the risk of heart failure by 22%, stroke by 30%, heart attack by 19% and pneumonia by 15%.
Flu vaccination does not require behaviour change or a daily intervention, yet it prevents cardiovascular events as well as as other evidence-based approaches such as statin therapy, antihypertensive therapy, and smoking cessation.
| This article is contributed by Immunise4Life (IFL), a collaboration of the Ministry of Health Malaysia with the Malaysian Paediatric Association (MPA) and the Malaysian Society of Infectious Diseases & Chemotherapy (MSIDC).
The article has been edited by HealthToday for publication on this website. For more information on flu, you can visit IFL’s website Act of Love (link opens in a new tab). |
References:
- Warren-Gash, C., Blackburn, R., Whitaker, H., McMenamin, J., & Hayward, A. C. (2018). Laboratory-confirmed respiratory infections as triggers for acute myocardial infarction and stroke: a self-controlled case series analysis of national linked datasets from Scotland. The European respiratory journal, 51(3), 1701794. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01794-2017
- Michos, E. D., & Udell, J. A. (2021). Am I getting the influenza shot too?: Influenza vaccination as post-myocardial infarction care for the prevention of cardiovascular events and death. Circulation, 144(18), 1485–1488. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.057534
- Modin, D., Jørgensen, M. E., Gislason, G., Jensen, J. S., Køber, L., Claggett, B., Hegde, S. M., Solomon, S. D., Torp-Pedersen, C., & Biering-Sørensen, T. (2019). Influenza vaccine in heart failure. Circulation, 139(5), 575–586. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036788
- Vamos, E. P., Pape, U. J., Curcin, V., Harris, M. J., Valabhji, J., Majeed, A., & Millett, C. (2016). Effectiveness of the influenza vaccine in preventing admission to hospital and death in people with type 2 diabetes. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l’Association medicale canadienne, 188(14), E342–E351. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.151059
- King, S. C., Fiebelkorn, A. P., & Sperling, L. S. (2020, November 2). Influenza vaccination: Proven and effective cardiovascular disease prevention. American College of Cardiology. https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2020/11/02/14/42/influenza-vaccination-proven-and-effective-cvd-prevention
- Vetrano, D. L., Triolo, F., Maggi, S., Malley, R., Jackson, T. A., Poscia, A., Bernabei, R., Ferrucci, L., & Fratiglioni, L. (2021). Fostering healthy aging: The interdependency of infections, immunity and frailty. Ageing research reviews, 69, 101351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101351