WORDS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DR VERNA LEE KAR MUN
 FEATURED EXPERT FEATURED EXPERTASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DR VERNA LEE KAR MUN Family Medicine Specialist IMU Healthcare |
WHY IS THE QDENGA VACCINE NECESSARY? WE ALREADY HAVE PREVENTIVE MEASURES SUCH AS FOGGING TO PREVENT THE AEDES MOSQUITO FROM BREEDING.
Fogging is effective in killing the Aedes mosquitoes. Its effect is immediate, extending to an average of 72 hours.
Fogging Works, but There Are Some Drawbacks
While fogging has been the main means to mitigate dengue infection in Malaysia, however, health offices are usually informed after the infection have been notified. As a result, fogging by itself does not reduce severe dengue infection that requires hospitalizations.
Furthermore, the resistance of the Aedes mosquitoes to insecticides is increasing. This decreases the effectiveness of fogging to control the population of these mosquitoes.
The Role of Dengue Vaccines
On the other hand, dengue vaccines have been proven to be effective in reducing the numbers of severe dengue infection requiring hospitalizations.
THERE WAS SOME CONTROVERSY WITH REGARDS TO THE SAFETY PROFILE OF THE PREVIOUS DENGUE VACCINE. SHOULD WE BE CONCERNED ABOUT THE QDENGA VACCINE?
Just like any new drug or new medical technology, there is very limited data from clinical practice in the early days. There would be many concerns.
Dengvaxia, the First Dengue Vaccine
The first dengue vaccine, Dengvaxia, was approved in April 2018.
It is safe in persons who have had dengue virus infection in the past (seropositive individuals), but it also increases the risk of severe dengue in those who experience their first natural dengue infection after receiving their vaccination (seronegative individuals).
Hence, pre-vaccination screening for past dengue infection is recommended before one receives the Dengvaxia vaccine. Only people with evidence of past dengue infection—indicated by the presence of dengue IgG antibody in their blood—would receive this vaccination.
About the Newest Vaccine, Qdenga
A second vaccine for dengue, Qdenga, received prequalification from the World Health Organization (WHO) on 10 May 2024.
Is it safe?
- Overall, during the clinical trials, the vaccine was well tolerated. The most frequent reported vaccine-related adverse events were injection site itchiness, bruising, and fever.
- An excess of hospitalized dengue virus serotype 3 (DENV3) infections was reported among baseline seronegative children, but it was not statistically significant.
- There was also an excess of cases of severe dengue among seronegative vaccinees, all of which were caused by DENV3, but, again, the difference was not statistically significant.
- An increase in the risk of dengue infection requiring hospitalization or severe dengue due to DENV3 in vaccinated seronegative subjects cannot be conclusively ruled out. We probably need to wait for more data.
How about allergy reactions?
During the clinical trial, no cases of severe allergy reaction or anaphylaxis were observed.
However, cases of anaphylaxis associated with this new vaccine occurred following the vaccine’s introduction to children between the age of 10 and 14 years in Brazil since February 2024, with 16 cases were reported (4.4/100,000 doses administered), including 3 cases of anaphylactic shock (0.8/100,000 doses administered).
The currently approved package insert for the vaccine describes precautionary measures to mitigate the risk of anaphylaxis. A full assessment of the national immunization programme is underway.
THE QDENGA VACCINE IS SAID TO BE ABLE TO IMMUNIZE AGAINST ALL FOUR SEROTYPES OF DENGUE VIRUS. WHY IS THIS A GOOD THING?
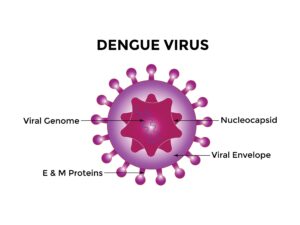
Dengue viruses belong to the genus Flavivirus.
The dengue virus. Click on the image for a larger, clearer version.
Flaviviruses are lipid-enveloped, single-stranded RNA viruses. The structural pre-membrane (prM) and envelope (E) proteins are embedded in the lipid envelope and are displayed on the surface of virions.
There are 4 dengue virus serotypes (DENV1, DENV2, DENV3, and DENV4); the serotypes share structural proteins (prM and E) but are genetically and serologically distinct.
Infection with 1 serotype induces sustained protection against the same serotype only. Although uncommon, an individual without a vaccine can be infected by each serotype for a total of 4 infections during their lifetime.
Serotypes and Infections
People who acquire a second dengue infection caused by a different serotype are at a higher risk for severe dengue once cross-protection induced by the first infection wanes.
Potential mechanisms for increased risk of severe dengue caused by a second infection include:
- Cross-reactive antibodies binding to a different DENV serotype, which then enable uptake in inflammatory cells. This leads to higher and more prolonged virus count in the blood circulation (higher temperature and prolonged fever) that induces imbalanced pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses often referred to as antibody-dependent enhancement.
- The action of the non-structural protein 1 (NS1) on the blood vessel wall or endothelium can trigger the release of active chemicals from immune cells.
- Both the above will result in endothelial hyperpermeability and vascular leak (leading to hypovolemic shock and bleeding).
How the Vaccine Is Beneficial
Both dengue vaccines are tetravalent live-attenuated vaccines.
The new vaccine, Qdenga, induces a broad spectrum of immune responses which include:
- Neutralizing antibodies with a 50% reduction against all 4 dengue virus serotypes.
- Cross-reactive antibodies that block the activity of the NS1 protein.
- Type-specific memory B cells to all four serotypes.
This means the vaccine can protect us from severe dengue infection by all the 4 serotypes. This is a good thing.