WORDS PROFESSOR DATO’ SETIA DR TAN HUI MENG
 FEATURED EXPERT FEATURED EXPERTPROFESSOR DATO’ SETIA DR TAN HUI MENG Consultant Urologist Subang Jaya Medical Centre (SJMC) |
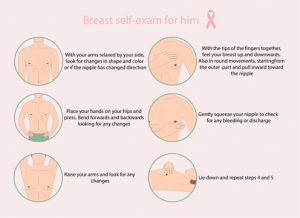
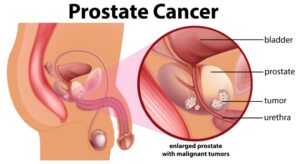
Prostate cancer is the third most common cancer among the male population in Malaysia after colorectal and lung cancer.
However, despite these staggering numbers, compared to breast cancer, prostate cancer screening appears to be a very controversial topic in medicine.
THE UNCERTAINTIES SURROUNDING PROSTATE CANCER
To date, most health professionals and the public at large are still lost and uncertain on how to go about preventive measures and the treatment of prostate cancer.
Sometimes, early prostate cancers are localized and contained within the prostate. The cancer grows very slowly and may not cause problems for years or may not even become advanced cancer. In cases like these, patients do not need to be treated.
THE RECOMMENDATION FOR PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING
In the United States, the Preventive Services Taskforce (USPSTF) gave a Grade C recommendation on screening for prostate cancer, which means individuals do not necessarily need to screen for prostate cancer unless they have concerns, and they should discuss their concerns with their physicians.
This recommendation came about to reduce the overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancers.
This decision, however, has resulted in an increasing trend of prostate cancer mortality and morbidity, causing much suffering and compromising the quality of life for patients.
THE CHALLENGE THAT WE FACE TODAY
The challenge today is to come up with a strategy to screen the right population and find lethal prostate cancers.
Equally important, we will also need new treatments that are less invasive and cause less morbidity in individuals.
IMPROVING SCREENING ACCURACY WITH mpMRI SCREENING
For more than 30 years, the medical profession did not make headway with regard to the diagnosis and management of prostate, other than developing robotic techniques and better radiotherapy to remove the tumours.
The Problem with the ‘Old System’
The diagnosis using systematic non-targeted transrectal ultrasound scan (TRUS) guided biopsy is highly inaccurate as it has high false negative rate. This is dangerous as it misses at least 50% of cancer.
The Development of mpMRI and Its Advantages
The transformative advancement in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer was the development of multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) of the prostate.
Using mpMRI as a triage can spare significant number of men from undergoing unnecessary prostatic biopsies and avoiding both physical and psychological trauma and morbidity, especially if TRUS biopsies are performed.
Many studies have confirmed that mpMRI is highly reliable in identifying more than 90% of men with clinically significant and lethal prostate cancer.
This method was reported to be much more sensitive (93%) in detecting prostate cancers compared to TRUS biopsies (48%).
MpMRI as a triage also detects much fewer clinically unimportant prostate cancer (54% fewer) compared to using the traditional TRUS biopsy.
In other words, mpMRI reduces overdiagnosis of clinically unimportant prostate cancer and improves the detection of clinically significant and deadly prostate cancer.
HENCE, TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN?
Many screening studies have shown that for men diagnosed with prostate cancers, whether they are treated or not, their survival outcome is generally over 10 years or so.
This shows that a majority of the men with prostate cancer detected by screening do not benefit from treatment.
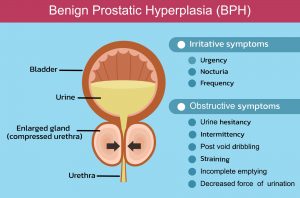
Instead, they suffer the consequences of treatment, like losing potency and experiencing urinary or rectal symptoms with occasional incontinence!
However, long-term studies show the benefits of screening are observed after consistent follow-ups for 12 years or more.
The Goteborg Randomised Cancer Prostate Screening Trial, done in Sweden, revealed that for men who have undergone over 14 years of follow-up and completed the screening, there was a 66% decrease in advanced prostate cancer in the screened population compared to the population of men who were randomized to the non-screening arm.
Therefore, one can conclude that men who have serial PSA screening and then treated if prostate cancer is detected have a 66% less chance of developing advanced prostate cancer—which often results in very painful bone metastases.
There was also a 56% lower mortality rate in the screened population.
Extrapolating from this result, in the Swedish population, PSA screening can save 5,700 out of 1 million screened men from dying of prostate cancer.
THE BEST WAY FORWARD
In summary, prostate cancer is still a significant life-threatening disease.
Early detection and early prediction of the disease are crucial, whereas screening in men with long life expectancies is beneficial.
Overdiagnosis and overtreatment issues can be addressed with targeted screening and biopsy only for at-risk patients. This aims for early detection & diagnosis of localized lethal prostate cancer, which is fully curable.
If diagnosed with non-lethal prostate cancer (especially low-grade cancer), individuals only require good active surveillance with a follow-up mpMRI. They should also repeat a biopsy of the prostate if necessary.
It is crucial for those with intermediate-grade prostate cancer (ISUP 2) or large volume low-grade prostate cancer (> 6mm core cancer tissue) to receive careful active surveillance paired with good clinical judgement and a follow-up mpMRI as well.
Men with localized lethal prostate cancer will need ablative treatment with surgery, radiotherapy or occasionally brachytherapy. Counselling for adverse events like erectile dysfunction and occasional urinary incontinence following ablative treatments should also be given.
MpMRI has greatly improved the diagnosis of clinically important prostate cancer, and better genomics will help predict the prognosis of the disease. Transperineal mpMRI – ultrasound fusion prostatic biopsy is the way forward. Focal therapy like HIFU, irreversible electrophoresis or targeted ablation will probably play an increasing role, especially for patients with favourable intermediate-risk or low-grade large-volume prostate cancer.







 DR KHINE PWINT PHYU
DR KHINE PWINT PHYU ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DR GANESH RAMACHANDRAN
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DR GANESH RAMACHANDRAN