WORDS DR JESRINA ANN XAVIER & DR LIEW KEAN YEW
FEATURED EXPERTS
 DR JESRINA ANN XAVIER DR JESRINA ANN XAVIERSenior Lecturer School of Management & Marketing Faculty of Business & Law Taylor’s University |
 DR LIEW KEAN YEW DR LIEW KEAN YEWPalliative Care Specialist Hospital Ampang |
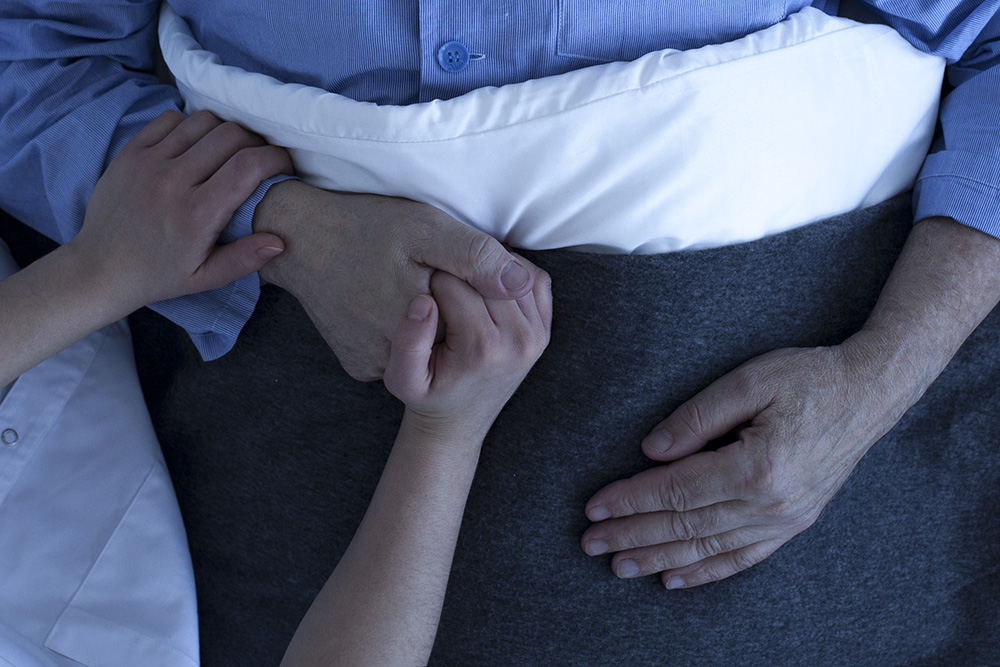
INTRODUCING PALLIATIVE CARE
- Palliative care is specialized medical care for people living with serious illnesses.
- It aims to improve the quality of life for patients and their families associated with life-threatening illnesses.
- Palliative care services were first offered in Malaysia in 1995, and they are gradually being included in the standard healthcare system.
RISING NEED OF PALLIATIVE CARE
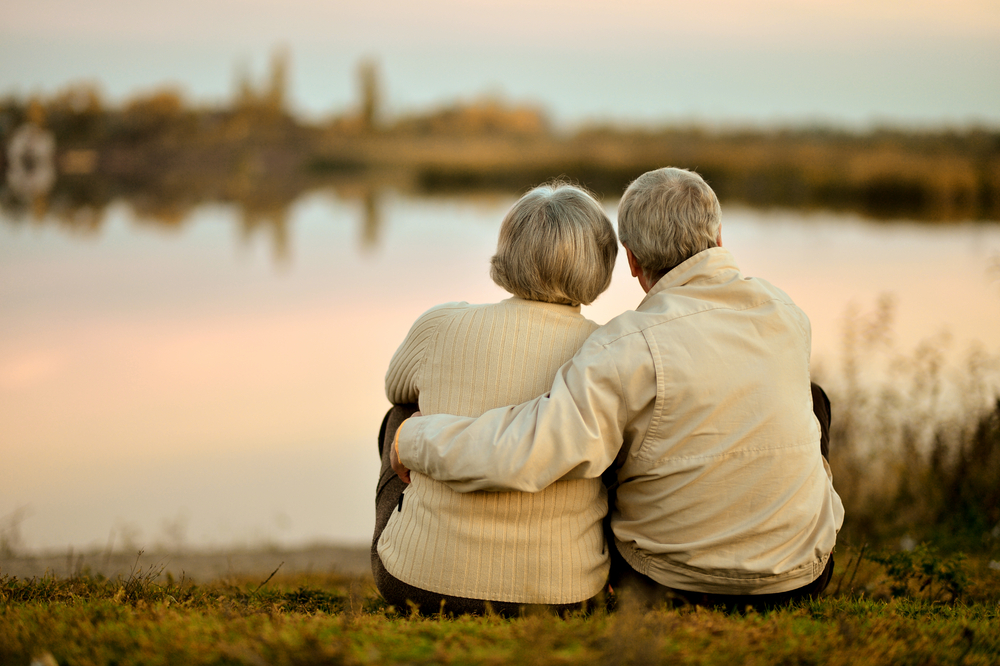
- The need for palliative care is on an upward trend all over the world due to the ageing population and the rising burden of chronic diseases.
- In Malaysia, the proportion of palliative care needs to deaths hovered at 71% in the observed years. By 2030, it is observed that the growth for palliative care specifically will increase to 240%.
- Sarawak, Perak, Johor, Selangor, and Kedah will become the top five Malaysian states with the highest needs in 2030.
COACHING IN PALLIATIVE CARE
- Coaching in palliative care refers to the practice of providing support, guidance, and education to individuals facing terminal or life-threatening illnesses, as well as their families and caregivers.
- It aims to improve quality of life by early detection and treatment of pain and symptoms.
- It also enables patients and their families to take an active role in choosing how they will be treated, reclaiming a sense of control over their lives.
THE BENEFITS OF COACHING IN PALLIATIVE CARE
Improved Communication and Expression Skills
- Anthony Grant, a revered psychologist, informs that coaching can be considered an emerging cross-disciplinary occupation, with the main goals being to improve performance, enhance well-being, and support organizational and individual change.
- Palliative care coaching adopts a comprehensive strategy, acknowledging that every person’s experience with illness is distinct and multifaceted.
- Coaching helps individuals develop their communication skills and express their needs, preferences, and concerns more effectively.
- It can lead to increased satisfaction in care outcomes.
Assists in Enhancing Patient Wellbeing
Through a coping mechanism, palliative care coaching assists patients and their families through goal setting, problem-solving, and symptom management.
Empowers Patients and Their Loved Ones to Make Informed Decisions
- Making decisions about treatment options, advance care planning, and end-of-life care is rather challenging when undergoing treatments.
- By providing information, the clarification of options, and assistance in weighing the advantages and disadvantages of various possibilities, coaching makes it easier for patients to advocate for their rights and choices.
Providing Patient-Centered Care
- Coaches can deliver patient-centered care that respects people’s cultural backgrounds, attitudes, and beliefs.
- Palliative care coaching helps patients, families, and healthcare professionals coordinate and collaborate, which promotes continuity of treatment to achieve shared objectives.










 DR SAPNA SHRIDHAR PATIL
DR SAPNA SHRIDHAR PATIL DR AMEYA ASHOK HASAMNIS
DR AMEYA ASHOK HASAMNIS PROFESSOR DR WEE LEI HUM
PROFESSOR DR WEE LEI HUM


 DR AISHAH MOHD HAFIZ
DR AISHAH MOHD HAFIZ DR DURGA VETTIVEL
DR DURGA VETTIVEL


 FEATURED EXPERT
FEATURED EXPERT