Recently, Roche Pharmaceuticals and Roche Diagnostics cemented a partnership with Premier Integrated Labs with the signing of a memorandum of understanding (MOU). This MOU is effective from November 2023.
The objectives of this partnership include improving patient access to comprehensive genomic profiling or CGP as well as promoting greater awareness and understanding of CGP among Malaysians.
 MS HENG CHAI YIN MS HENG CHAI YINGeneral Manager Roche Diagnostics (M) Sdn Bhd |
“While awareness and understanding are crucial, our ultimate goal is to ensure that CGP is accessible to all patients in Malaysia. It is about providing every patient with the best possible chance for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan,” says Ms Heng Chai Yin, the General Manager of Roche Diagnostics Sdn Bhd.
WHAT IS COMPREHENSIVE GENOMIC PROFILING (CGP)?
With a single test, comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP) can analyse a broad panel of genes that is known to drive cancer growth. This type of testing produces comprehensive patient reports with broad and deep assessments of the possible underlying cancer drivers.1
HOW CGP PLAYS A KEY ROLE IN PRECISION MEDICINE
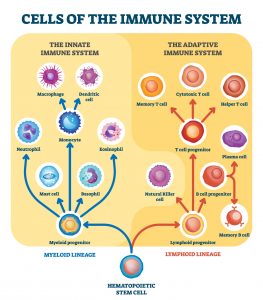
Precision medicine involves the use of personalized treatments for an individual with regards to a disease.2
Different people can respond differently to the same medication for the same disease, and there are many possible factors that are responsible for these differences.
Hence, a big part of precision medicine involves the identification of these differences through investigative methods such as in the image below.

HOW CGP CAN IMPROVE THE PRECISION OF CANCER TREATMENT IN MALAYSIA
 MS DEEPTI SARAF MS DEEPTI SARAFGeneral Manager Roche (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd |
According to Ms Deepti Saraf, CGP holds the key to unlocking the full potential of personalized medicine. It allows us to explore the genetic makeup of individuals, thereby enabling more precise and tailored treatment approaches.
Let’s look at lung cancer as an example.
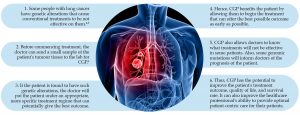
CGP IS DIFFERENT FROM CONVENTIONAL GENOMIC TESTS
Ms Deepti Saraf points out that, unlike those genomic tests in the market that let you know about your genes and ancestry, CGP is more of a diagnostic tool that empowers doctors, especially oncologists, to create the most optimal personalized treatments for their patients based on available data.
 EN HAREEFF MUHAMMED EN HAREEFF MUHAMMEDChief Executive Officer Premier Integrated Labs |
En Hareeff Muhammed brings up that, with the wealth of genomic data obtained through the use of CGP, databases can be created to analyse which treatments would work best for different groups of patients.
This goes back to Ms Deepti Saraf’s statement that CGP allows healthcare professionals to design the best personalized treatments for their patients. They can do this by using the information found in the database to help shape their decisions.
“It’s not just useful for the patients and saves time,” En Hareeff elaborates. “It also supports doctors in making better decisions.”
This is an educational article brought to you by

References:
- Foundation Medicine. (n.d.). Why comprehensive genomic profiling? https://www.foundationmedicine.com/resource/why-comprehensive-genomic-profiling
- König, I. R., Fuchs, O., Hansen, G., von Mutius, E., & Kopp, M. V. (2017). What is precision
medicine?. The European respiratory journal, 50(4), 1700391. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00391-2017 - Omics-based clinical discovery: Science, technology, and applications. (2012, March 23). In C.M. Micheel, S.J. Nass, & G.S. Omenn (Eds), Evolution of translational omics: lessons learned and the path forward (p. 33). National Academies Press (US). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK202165/
- Tan, J., Hu, C., Deng, P., Wan, R., Cao, L., Li, M., Yang, H., Gu, Q., An, J., & Jiang, J. (2021). The predictive values of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring uncommon EGFR mutations-the mutation patterns, use of different generations of EGFR-TKIs, and concurrent genetic alterations. Frontiers in oncology, 11, 646577. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.646577
- American Lung Association. (2022, November 17). EGFR and lung cancer. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/lungcancer/symptoms-diagnosis/biomarker-testing/egfr











 FEATURED EXPERT
FEATURED EXPERT
 FEATURED EXPERT
FEATURED EXPERT